If you’re just stepping into the digital world, you’ve probably heard tons of people say things like “You need SEO to rank on Google” and “SEO is the key to online success.” But what is SEO? Why are people still talking about it in 2025? How does it even work?
SEO 101, or Search Engine Optimization 101, is intended for beginners to learn how websites show up on Google and how businesses acquire customers online. Whether you are running a small blog, an eCommerce store, or a multinational business, SEO is essential for reaching the right audience with your content.
This guide is your step-by-step SEO roadmap. We are going to cover everything from SEO jargon to technical SEO, local SEO, and international SEO, and let’s not forget current trends in 2025. By the end of this guide, you will not only understand SEO but also be able to implement it for your business or website for a real outcome.

SEO is the abbreviation for Search Engine Optimization. In layman’s terms, it is the act of increasing your web page’s visibility on search engines, such as Google, Bing, or Yahoo! So, for example, if someone goes to a search engine and types in “Best pizza near me” or “How to fix a broken laptop screen,” it brings up a list of sites that match the request.
SEO is what gets the site to show up on the first page of search results, and the better you rank, the more likely the user will click on your site instead of your competitor’s. Think of SEO as the bridge between your business and your customers.
At its core, SEO is about:
- Understanding what people search for (keywords).
- Creating useful and engaging content that answers their questions.
- Making your website technically strong so Google can easily read and index it.
- Building authority and trust so that search engines prefer your site over others.
You might wonder, “Is SEO still important in 2025 when we have AI tools, social media, and voice assistants?” The answer is a big YES.
Here’s why SEO is still the king of digital marketing:
- Organic Traffic is Free: Unlike ads, you don’t pay per click once you rank.
- Trust Factor: People trust Google’s organic results more than paid ads.
- AI + Search Engines Work Together: Even with AI chatbots, most answers still come from indexed web pages. Learn more about optimizing for voice search in our Voice Search SEO 2025 guide.
- Local and Global Reach: Whether you want to rank in your city or worldwide, SEO adapts to your needs.
- Evergreen Marketing: Good SEO done today can bring traffic for years.
To understand search engine optimization (SEO), you need to understand how Google works. Think of Google as a massive library with billions of books (websites). When you search for something in Google, the search engine tries to find you the best and most relevant result. There are three steps to this process:
- Crawling – Google sends its bots (spiders) to “read” and collect information from websites.
- Indexing – The collected information is stored in Google’s database (like a library catalog).
- Ranking – When you search, Google’s algorithm decides which websites are most useful and shows them in order.
For example:
- If you search “buy running shoes online,” Google will show eCommerce sites like Nike, Adidas, or Amazon because they are relevant, trusted, and optimized for that keyword.
- If your small shoe store has good SEO, you could also appear on the first page!
Now that you understand the workings of search engines, let’s move on to the basics of SEO 101. These are the fundamentals that every beginner needs to know before doing the advanced tactics.
These are the basic terms you need to become familiar with. Knowing these terms will allow you to read SEO guides, use SEO tools, and communicate with specialists.
- Keywords: The words people type into Google (e.g., “best Italian restaurant in New York”).
- Search Intent: The purpose behind a search (to buy, to learn, to compare, etc.).
- SERP: Search Engine Results Page (the list of results Google shows).
- Organic Ranking: Your website’s position in Google without paid ads.
- CTR (Click-Through Rate): Percentage of people who click your website when it shows up.
- Bounce Rate: Percentage of visitors who leave your site quickly (Google sees this as bad).
Think of On-Page SEO as your content, Off-Page SEO as your reputation, and Technical SEO as your website’s foundation. SEO is often divided into three main categories:
1. On-Page SEO—Everything you do on your website to make it Google-friendly.
- Keywords in titles, headers, and content.
- Internal linking between pages.
- Optimized images, meta tags, and mobile-friendly design.
2. Off-Page SEO – Actions outside your website that increase authority.
- Getting backlinks from other websites.
- Social media engagement.
- Brand mentions on the web.
3. Technical SEO – Website performance and behind-the-scenes structure.
- Fast loading speed.
- Secure (HTTPS) websites.
- XML sitemap & robots.txt.
- Fixing crawl errors.
SEO isn’t merely a technical job; rather, it is a fundamental part of digital marketing. Practically every digital channel is touched by SEO. In essence, SEO is the backbone of digital marketing because it makes everything else perform better:
- Content Marketing: Blogs, videos, and guides rely on SEO to get discovered.
- Social Media Marketing: Social shares increase visibility and indirectly boost SEO.
- Email Marketing: SEO drives new visitors who later join your email list.
- Paid Ads (SEM): While ads bring instant traffic, SEO brings long-term results.
To understand SEO 101, you need to be familiar with the four core pillars of SEO. You can think of SEO as building a house because when you combine all four pillars, your website will become strong, visible, and trusted by Google.
- Keyword research is the blueprint.
- Content optimization is the walls and design.
- Technical SEO is the foundation.
- Off-page SEO is the reputation and trust from your neighbors.
Keyword research is the first and most important step in SEO. It tells you what your audience is searching for and how to target them.
Short-Tail vs Long-Tail Keywords
Short-Tail Keywords → 1–2 words, very broad, high search volume, but also high competition.
- Example: “shoes”, “SEO”.
Long-Tail Keywords → 3+ words, more specific, lower competition, and higher conversion rate.
- Example: “best running shoes for flat feet 2025”.
For beginners, long-tail keywords are the best choice because they’re easier to rank for.
Using Tools
There are many tools that help you find keywords:
- Google Keyword Planner – Free tool for basic keyword ideas.
- SEMrush & Ahrefs – Paid tools for deep competitor analysis and keyword gaps.
- AnswerThePublic – Shows questions people ask about a topic.
- Google Autocomplete & People Also Ask – Quick free ways to find keyword ideas.
How to Find Low Competition Keywords
- Type your keyword into Google.
- Check the website’s ranking on page one.
- If you see big brands like Amazon or Wikipedia, it’s tough.
- If you see small blogs or forums, that’s a low-competition keyword you can target.
Always match the search intent. If someone searches “how to do SEO step by step”, they want a guide, not a sales page.
Once you know your keywords, the next step is optimizing your content so that both people and Google love it.
Title Tags, Meta Descriptions, and Headers
- Title Tag: Appears in Google results. Must include your keyword.
- Meta Description: Short summary under the title in search results. Should be engaging and keyword-rich.
- Headers (H1, H2, H3): Break your content into sections. Use keywords naturally.
Example:
- Title: “SEO 101 Guide for Beginners in 2025 – Step-by-Step Tips”
- Meta: “Learn SEO basics in 2025 with this beginner-friendly guide. Covers keyword research, content optimization, technical SEO, and more.”
Keyword Placement & Natural Flow
- Put your keyword in the first 100 words.
- Use it in headers (H2/H3).
- Sprinkle it 2–3 times naturally in the content.
- Avoid keyword stuffing (Google will penalize you).
EEAT (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness)
Google now values EEAT signals more than ever in 2025:
- Experience: Show that you’ve used or tested what you’re writing about.
- Expertise: Provide in-depth knowledge.
- Authoritativeness: Get backlinks and mentions from trusted sites.
- Trustworthiness: Secure website (HTTPS), transparent contact info, and real reviews.
Even if your content is great, if your website has technical issues, Google may not rank it well.
Mobile-Friendly Design & Core Web Vitals
- Most searches now come from mobile.
- Your website must load fast and look good on phones.
- Core Web Vitals (Google’s user experience signals):
- Loading speed
- Interactivity (click response time)
- Visual stability (no shifting content)
Site Speed Optimization
- Use compressed images (WebP format).
- Enable caching.
- Use a fast hosting provider.
- Minimize JavaScript & CSS files.
Proper URL Structure
- Keep URLs short and clean.
- Example: www.example.com/seo-101-guide instead of www.example.com/index.php?id=12345.
XML Sitemap & Robots.txt
- XML Sitemap → A file that lists all important pages for Google to crawl.
- Robots.txt → Tells Google which pages NOT to crawl (like admin pages).
Off-page SEO is all about building authority outside your website. Google uses backlinks (links from other sites) as a sign of trust.
Backlinks and Why They Matter
- A backlink is like a “vote of confidence” from another site.
- More quality backlinks = higher chances of ranking.
Guest Posting, Outreach & Digital PR
- Write guest articles on other blogs in your niche.
- Reach out to influencers and websites for mentions.
- Use digital PR (press releases, online news mentions).
Social Signals & Brand Mentions
- Google considers brand presence across the web.
- Active social media profiles indirectly boost SEO.
- Even unlinked brand mentions can help build trust.
Not every business aims to achieve a global ranking. Some merely want to reach local customers, such as restaurants, gyms, dentists, and plumbers. This is where Local SEO 101 is important. Local SEO will enable your business to show up when searching with a location-based keyword, such as “near me,” “in [city],” or “closest to me.” It is important even in 2025 because consumers use mobile searches and voice-based assistants more than ever to look for offers locally.
Local SEO is the process of optimizing your website and business profile so that it appears in local search results.
Example:
- If someone searches “best pizza near me” in New York, Google will show local pizzerias in the area, not in Los Angeles.
- If your restaurant has good Local SEO, it will show up in Google Maps and the Local 3-Pack (the top 3 map listings on Google).
Why it’s important:
- 50% of local searches result in a store visit within 24 hours.
- 78% of mobile searches for local businesses result in offline purchases.
- Local SEO = free advertising for businesses targeting nearby customers.
One of the strongest tools available for local SEO is the Google Business Profile (GBP), which was previously known as Google My Business (GMB). An optimized GBP profile can drive more traffic to your business than your website sometimes!
Steps to optimize:
- Claim your profile at Google Business Profile.
- Fill in accurate business info (name, address, phone number, website, hours).
- Add high-quality photos of your business, staff, and products.
- Select the right categories (e.g., “Italian Restaurant,” “Digital Marketing Agency”).
- Post regular updates (offers, events, new products).
- Enable messaging and booking if applicable.
Local Citations & NAP Consistency
A local citation is any mention of your business with your Name, Address, and Phone number (NAP) on the internet. The NAP must be the same everywhere. If Google sees your address listed differently from website to website, they could lower your ranking!
Examples:
- Online directories like Yelp, Yellow Pages, TripAdvisor.
- Social media pages.
- Local chamber of commerce websites.
Getting Local Reviews for Trust & Ranking
Reviews are a major ranking factor for local SEO. They also have an influence on buying decisions. Businesses with good reviews tend to get more clicks, more trust, and a higher Google ranking.
- Ask happy customers to leave reviews on your Google Business Profile.
- Reply to all reviews—positive or negative (shows professionalism).
- Encourage reviews on Yelp, Facebook, and industry-specific platforms.
- Never fake reviews (Google can detect spammy behavior).
Example:
Let’s say you run a small pizza restaurant in Chicago. Here’s how Local SEO helps:
- Keywords: Target “best pizza in Chicago” or “pizza near me Chicago.”
- Google Business Profile: Add mouth-watering food photos, business hours, and location.
- Citations: Ensure Yelp, TripAdvisor, and Zomato list your business with the same NAP.
- Reviews: Encourage satisfied customers to leave 5-star Google reviews.
- Local Content: Write a blog post like “Top 5 Pizza Spots in Chicago – Why Ours Stands Out.”
If Local SEO 101 educates you to win in your city, International SEO 101 educates you to win in the global market. It’s for businesses that are targeting customers in different countries and/or languages: eCommerce stores, SaaS businesses, and travel websites are a few examples. Without effective international SEO, your content may be shown in the wrong country, in the wrong language, or not shown at all!
What Makes International SEO Different?
Unlike normal SEO, international SEO deals with:
- Languages → Optimizing for English, Spanish, French, Chinese, etc.
- Countries → Optimizing for USA, UK, India, or any other specific country.
- Search Behavior → People in different countries search differently.
For example:
- In the US, people may search “cheap flights.”
- In the UK, they may search “budget flights.”
- In Germany, they might search “günstige Flüge.”
Without international SEO, you might miss out on these customers.
Hreflang Tags & Multilingual Optimization
One of the most important international SEO elements is the hreflang tag.
- What it does: Tells Google which version of your page to show in each country/language.
Example:
- English (US) → hreflang=”en-us”
- English (UK) → hreflang=”en-gb”
- Spanish (Spain) → hreflang=”es-es”
Country-Specific Domains vs Subfolders
When targeting multiple countries, you must decide how to structure your website:
1. Country Code Top-Level Domains (ccTLDs)
- Example: example.uk, example.fr, example.de
- Pros: Strong local signal, builds trust in that country.
- Cons: Expensive, harder to manage multiple sites.
2. Subdomains
- Example: uk.example.com, fr.example.com
- Pros: Easy to set up, flexible.
- Cons: Google treats them as separate websites.
3. Subfolders (Recommended for beginners)
- Example: example.com/uk/, example.com/fr/
- Pros: Easier to manage, stronger domain authority.
- Cons: Requires a good technical setup.
Cultural & Language Differences in SEO
SEO isn’t just mapping out keywords; SEO is about culture. Cultural research and understanding the behavior of the local area are vital before launching in a new country.
- Example: In Japan, searchers prefer very polite and formal content.
- In the US, shorter, casual, and direct content works better.
- In Middle Eastern countries, right-to-left language support is critical.
Common Mistakes in International SEO
Many beginners fail at international SEO because they:
- Use auto-translators → Leads to poor grammar and wrong meanings.
- Don’t set hreflang tags → Users see the wrong language version.
- Copy-paste content across languages → Google may treat it as duplicate content.
- Forget about local search engines → In China, Baidu dominates; in Russia, it’s Yandex.
- Ignore local regulations → For example, GDPR compliance in Europe.
Local SEO is used for cities, and international SEO is for many countries. National SEO is for businesses that want to dominate one country. National SEO is good because it allows you to target customers across a country instead of just locally.
Example:
- An eCommerce store that only ships within the UK.
- A law firm offering services only in the USA.
- A coaching company targeting just one country’s audience.
Single Country Focus (e.g., SEO for UK Only)
When your business only serves one country, your SEO strategy should be laser-focused on that country’s audience.
For example:
- If you’re a UK-based online store, you want to appear for searches across the whole UK, not just in London or Manchester.
- If you’re in the US, you want to rank nationwide, even if your office is in one state.
This means using country-specific keywords, targeting national competitors, and tailoring your content for that country’s culture.
National Keyword Targeting
Unlike local keywords, which include cities (“best pizza in Chicago”), national keywords target the whole country.
Examples:
- Local Keyword: “plumber in Miami.”
- National Keyword: “best online plumbing services USA.”
- Competitor Analysis Within the Country
To be successful in national SEO, you have to learn about your competitors at the country level. Understanding how and why they rank for their keywords will help you be better at ranking.
Steps:
- Search your target keyword on Google.
- Identify which national companies rank on page one.
- Analyze their:
- Content structure (what topics do they cover?).
- Backlinks (where are they getting links from?).
- Technical SEO setup (speed, mobile-friendly, schema).
- Use tools like SEMrush, Ahrefs, and SimilarWeb for competitor tracking.
Content Strategy for National Audience
Content for national SEO should appeal to a wide audience rather than just one city.
Examples:
- Instead of “Best gyms in New York”, write “Top 10 Gyms in the USA for 2025.”
- Instead of “Affordable dentists in Manchester”, write “How to Find Affordable Dental Care in the UK.”
Building Authority in One Country
To rank at the national level, you need to build strong authority signals in that country. The stronger your authority within one country, the more Google will trust your site for national rankings.
How to do it:
- National Backlinks: Get links from top newspapers, magazines, and blogs in your country.
- Example: Guest posts on Forbes UK or The Guardian.
- Country-Specific Directories: List your business in national directories.
- Local + National PR: Issue press releases or collaborate with influencers.
- Social Media Reach: Target audiences across the entire country with campaigns.
SEO can be intimidating at first for beginners, but the great thing is that there are tools to help make the process much easier. They can help you track performance, identify keywords, check backlinks, and understand your site better.
Google Search Console (SEO 101 Google Tool)
Google Search Console is a free tool that will show how well your site works in search. It will show you what keywords are bringing in traffic, any indexing issues if there are any, and how many clicks and impressions you are receiving. For a beginner, it is something you should check every day to track growth.
Google Analytics 4 Basics
Google Analytics 4 (GA4) allows you to understand your visitors’ engagement and how they interact with your website, including where users are coming from to visit your site, how long they stay on your site, what pages on your website get the most engagement, etc. This data can help you better your SEO and increase conversions.
Free vs Paid SEO Tools
There are a ton of free options like Google Keyword Planner, Ubersuggest, and AnswerThePublic, which are good for beginners. There are also lots of paid options like SEMrush, Ahrefs, and Moz, which will help you identify key elements, engagement with competitors, and deeper keyword analysis for long-term growth.
If you prefer learning visually, this video will give you a clear overview.
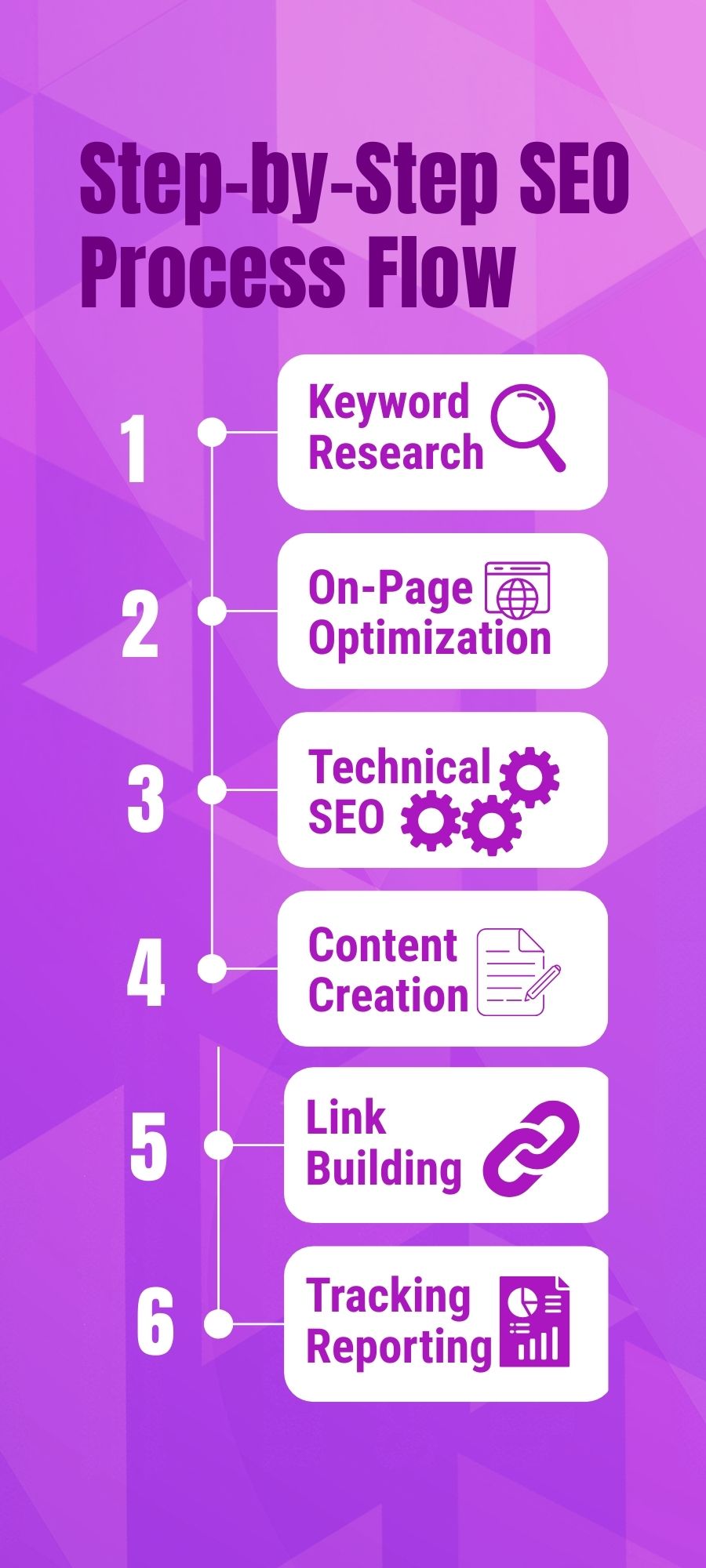
If you’re just starting your SEO journey, it can feel overwhelming. That’s why having a step-by-step checklist makes everything easier. Think of this as your SEO roadmap for 2025. Follow these steps in order, and you’ll have a strong foundation for SEO success.
Step 1: Set Up the Basics
- Create a Google Search Console account to track indexing and performance.
- Set up Google Analytics 4 to measure traffic and behavior.
- Install an SEO plugin (Yoast SEO, Rank Math, or All in One SEO) if using WordPress.
- Ensure your website uses HTTPS (secure SSL certificate).
Step 2: Do Keyword Research
- Use tools like Google Keyword Planner, SEMrush, or Ahrefs.
- Focus on long-tail keywords that are easier to rank.
- Match content with search intent (informational, commercial, or transactional).
- Make a list of primary and secondary keywords for each page.
Step 3: Optimize On-Page SEO
- Write title tags with your target keyword.
- Craft meta descriptions that encourage clicks.
- Use H1 for main title and H2/H3 for subheadings.
- Include your keyword naturally in the first 100 words.
- Add internal links to other relevant pages.
Step 4: Create High-Quality Content
- Write content that answers user questions in detail.
- Use simple, clear language for beginners.
- Add images, videos, and infographics to keep readers engaged.
- Apply EEAT principles (show experience, expertise, authority, and trust).
- Update old content regularly with fresh info.
Step 5: Strengthen Technical SEO
- Make sure your site is mobile-friendly.
- Optimize site speed with caching and image compression.
- Fix broken links and crawl errors.
- Submit an XML sitemap to Google Search Console.
- Use clean, descriptive URLs with keywords.
Step 6: Build Off-Page SEO (Backlinks & Authority)
- Reach out to blogs for guest posting opportunities.
- Build backlinks from trusted websites in your niche.
- Encourage brand mentions on social media and forums.
- Use digital PR strategies like press releases.
Step 7: Focus on Local SEO (If Applicable)
- Claim and optimize your Google Business Profile.
- Make sure your NAP (Name, Address, Phone) is consistent.
- Get local citations from directories.
- Collect Google reviews from happy customers.
Step 8: Expand with International/National SEO (If Needed)
- Add hreflang tags for multilingual sites.
- Use subfolders or country domains for different regions.
- Research cultural differences before expanding globally.
- Target country-wide keywords for national SEO.
Step 9: Track & Measure Results
- Use Google Search Console to monitor keyword rankings.
- Check Google Analytics 4 for user behavior.
- Compare your site with competitors using SEMrush or Ahrefs.
- Adjust your strategy every month based on data.
Step 10: Stay Updated with SEO Trends
- Follow the official Google Search Central Blog.
- Keep up with algorithm updates.
- Watch SEO experts on YouTube or Twitter (X).
- Test new strategies (voice SEO, AI-driven search optimization, video SEO).

When learning the fundamentals of SEO 101, it’s also important to understand how strategies are evolving. You can explore more in this guide on Traditional SEO vs AI SEO.
Congratulations, you’ve now walked through the complete SEO 101 Guide for Beginners. By now, you should understand what SEO is, why it matters in 2025, and how search engines like Google crawl, index, and rank websites.
We covered the fundamentals of SEO, including keyword research, on-page, off-page, and technical SEO, as well as Local SEO, International SEO, and National SEO strategies. You’ve also got a step-by-step SEO checklist to follow, making it easier to take action.
Here’s the truth: SEO is not a one-time job, it’s an ongoing process. Search engines change, user behavior changes, and competitors always fight for the top spot. But if you apply what you’ve learned in this guide consistently, you’ll be way ahead of most beginners.
Remember:
- Start small, master the basics.
- Be consistent with content and optimization.
- Always focus on user experience first, Google second.
- SEO is like planting a tree: the sooner you start, the sooner you’ll enjoy the long-term benefits.
Learning SEO 101 is only the first step — the real success comes when you apply it effectively. If you’re ready to grow your business with expert SEO strategies, our team at Concept Beans can help. From keyword research to complete optimization, we’re here to boost your visibility in 2025 and beyond. Contact us today to start your SEO journey with professionals.
What is SEO in simple words?
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is the process of improving your website so it shows up on Google when people search for products, services, or information. In simple terms, SEO helps you get free traffic from Google.

Why is SEO important in 2025?
In 2025, SEO is still important because people use search engines daily to find answers, services, and products. Unlike paid ads, SEO brings long-term, cost-free traffic and builds trust with your audience.

How long does SEO take to show results?
SEO usually takes 3–6 months to see noticeable improvements. However, for very competitive keywords, it may take 6–12 months. Patience and consistency are key.

What is the difference between Local SEO and International SEO?
- Local SEO targets customers in a specific city or area (e.g., “dentist near me”).
- International SEO targets multiple countries and languages (e.g., eCommerce stores shipping worldwide).

Do I need coding knowledge for SEO?
No, most beginners can do SEO without coding. Tools, plugins, and CMS platforms like WordPress make it easy. However, basic HTML knowledge can help with technical SEO.

What are the 3 main types of SEO?
- On-Page SEO – Optimizing content and keywords.
- Off-Page SEO – Building backlinks and authority.
- Technical SEO – Improving site structure, speed, and crawlability.

Can SEO work without content?
No. Content is the foundation of SEO. Without content, there’s nothing for Google to index. Quality blog posts, guides, videos, and product descriptions are essential for ranking.

What’s the difference between SEO and SEM?
- SEO = Free, organic rankings on Google.
- SEM (Search Engine Marketing) = Paid ads on Google (Pay-Per-Click).
Both can work together for better results.

Will AI replace SEO in the future?
AI won’t replace SEO, but it will change how SEO works. AI tools help create content and improve keyword research, while Google’s AI-driven search still relies on optimized websites. SEO will evolve, but it’s not going away.


I am Wajiha Ghazal, Co-Founder of Concept Beans Pvt Ltd and AI Digital Marketing Expert and With a focus on AI-powered tools, strategies, and automation, I help businesses scale and thrive online. My expertise spans AI-driven SEO, paid advertising, content marketing, and data-led growth hacking. Passionate about the future of digital marketing, I actively share insights through global platforms and training sessions.



2 comments
This is informative. Thank you for sharing this.
Fantastic beginner‑friendly SEO 101 Guide
This article clearly explains the core concepts of SEO — from keywords and technical SEO to on‑page and off‑page optimization — in a way that’s easy to follow. I especially liked how it breaks down practical steps for beginners to implement right away. Thanks for sharing these insights!